Low charge refrigeration systems
Traditional refrigeration systems containing synthetic refrigerants and used at cold stores, shops, and other similar facilities:
- entail a high risk of becoming obsolete which results in the non-compliance with the current environmental legislation (and, as consequence, need to replace it);
- contain a large refrigerant charge;
- consume much electrical energy and require heavy operating expenses.
Innovative low charge refrigeration systems are the solution that does not have such disadvantages and is easy to design and install.
These systems:
- are energy efficient;
- are of a standard design;
- are reliable, easy-to-operate and ready for operation;
- can recover discarded heat in full;
- can be installed using plastic or other sanitary pipes.
You can see an example of such a system in the figure:
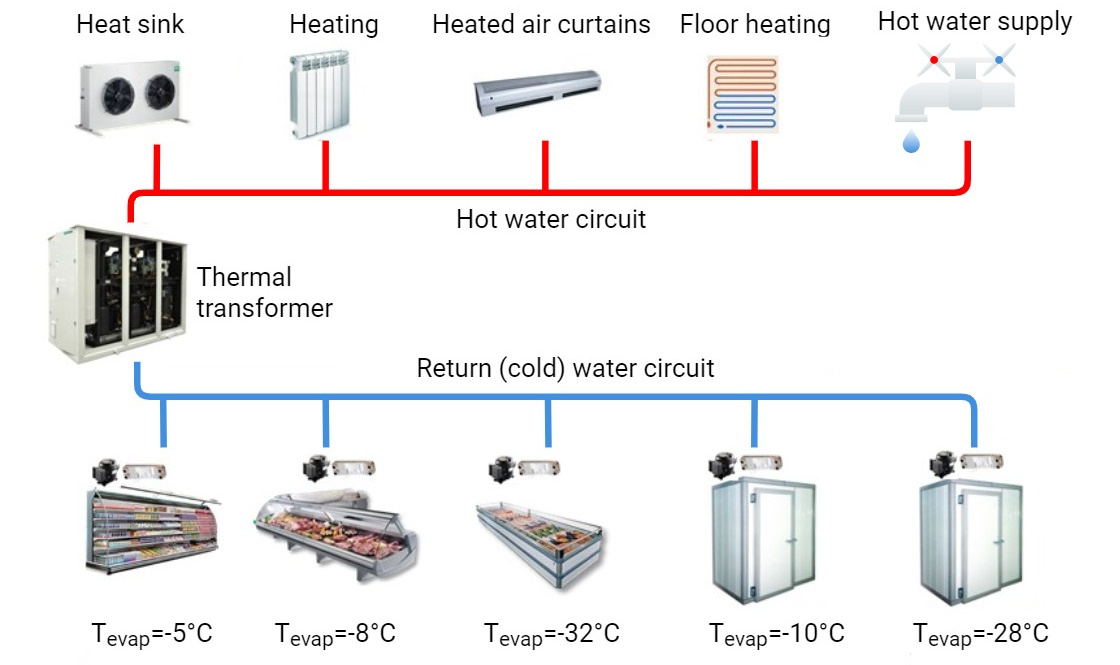
A low charge refrigeration system is a thermal transformer with:
- a return (cold) water circuit with individual modules that usually are packaged condensing units or low charge chillers that supply refrigerating chambers, freezers, etc.,
- a heat user circuit with hot water users that usually are heating and hot water systems (including those used for to serve processes), fish farming pools;
- a heat sink circuit with a dry-cooler or air condenser.
The thermal transformer is a dedicated refrigeration system that maintains the temperature in the cold water circuit and converts low-grade heat of the return water (+25°C) to supply heat users with +60–65°C water.
The thermal transformer:
- controls the performance of a refrigeration system depending on the load and environmental conditions;
- distributes the generated heat between the heat recovery system and the heat extraction system;
- ensures backup in case of fault;
- controls the temperature of a heat carrier in the heat recovery system.
Low charge systems are controlled automatically, do not need adjustment or external control during installation or operation.
Thermal transformers use R-744 (CO2), R-717 (ammonia), R-134a, R-513A, R-450A, other substances, and blends.
Their heat capacity varies from 30 to 750 kW, and the refrigeration capacity from 20 to 500 kW.
The constant temperature in the return (cold) water circuit ensures constant condensation temperature in individual modules: 20°C at the inlet and 25°C at the outlet of condensers of packaged condensing units and chillers.
Individual modules (packaged condensing units) supply refrigeration to each unit of refrigeration equipment. The selection of a module depends only on two parameters: refrigerant boiling temperature and refrigeration capacity. Modules function independently of each other and do not influence the operation of each other.
Modules are fitted with sealed compressors and are charged with R-717 (ammonia), R-290 (propane), R-449A, R-452A, other substances, and blends. Their refrigeration capacity and evaporation temperature can vary greatly: from 10 to 150 kW, and from -35 to +4°C. A module can be installed on a refrigerator or next to it. It is small so it can easily be concealed with decorative fixtures.
All connections are factory-made, and only two refrigerant lines (liquid and vapor) must be connected on the site, so the likelihood of a mistake is minimum.
A dry-cooler to sink excess heat can be located at any place behind a noise screen.
Modules are connected via water circuits of plastic or other sanitary pipes that can easily be laid by a sanitary technician.
Without limitations that are typical for the systems with standard refrigeration pipelines, low charge systems can easily be installed at any cold store.
Additional materials
- Bitzer support for low-charge ammonia chiller
- Glycol systems offer best ammonia reduction in analysis of oil cooling and evaporators
- ATMO America: Evapco installs its first low-charge ammonia split systems in Nevada cold storage facility
- Packaged ammonia or CO2? Evapco now offers both
- CTS improves ultra-low-charge ammonia chiller performance with ejector
- Evapco Reports Installation of 100 Low-Charge Ammonia Packaged Units at 25 Sites
- Greater awareness needed on benefits of low-charge ammonia systems in Australia, says Scantec
- ATMO America: Cimco Ammonia System for Meat Processor an Early Example of ‘Net Zero’
- Mayekawa Installs First FUGU Ammonia Chillers in Germany, France & Spain
- German Brewery Chooses R290 Chiller for Production Site
- 26.01.2016, Press conference “Russian refrigeration industry and global environmental agreements”
- Demonstration project “Heat and refrigeration supply system for a mini-hotel with a store and laundry using hydrocarbon refrigerants (in Russian)
- 25.11.2015, Demonstration model of a mini-hotel with a store and laundry using natural refrigerants. Training report


